A name collision occurs when a user attempts to resolve a domain in one namespace, but it unexpectedly resolves in a different namespace. Name collision issues in the public global Domain Name System (DNS) cause billions of unnecessary and potentially unsafe DNS queries every day. A targeted outreach program that Verisign started in March 2020 has remediated one billion queries per day to the A and J root name servers, via 46 collision strings. After contacting several national internet service providers (ISPs), the outreach effort grew to include large search engines, social media companies, networking equipment manufacturers, national CERTs, security trust groups, commercial DNS providers, and financial institutions.
While this unilateral outreach effort resulted in significant and successful name collision remediation, it is broader DNS community engagement, education, and participation that offers the potential to address many of the remaining name collision problems. Verisign hopes its successes will encourage participation by other organizations in similar positions in the DNS community.
Verisign is proud to be the operator for two of the world’s 13 authoritative root servers. Being a root server operator carries with it many operational responsibilities. Ensuring the security, stability and resiliency of the DNS requires proactive efforts so that attacks against the root name servers do not disrupt DNS resolution, as well as the monitoring of DNS resolution patterns for misconfigurations, signaling telemetry, and unexpected or unintended uses that, without closer collaboration, could have unforeseen consequences (e.g. Chromium’s impact on root DNS traffic).
Monitoring may require various forms of responsible disclosure or notification to the underlying parties. Further, monitoring the root server system poses logistical challenges because any outreach and remediation programs must work at internet scale, and because root operators have no direct relationship with many of the involved entities.
Despite these challenges, Verisign has conducted several successful internet-scale outreach efforts to address various issues we have observed in the DNS.
In response to the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Number (ICANN) proposal to mitigate name collision risks in 2013, Verisign conducted a focused study on the collision string .CBA. Our measurement study revealed evidence of a substantial internet-connected infrastructure in Japan that relied on the non-resolution of names that end in .CBA. Verisign informed the network operator, who subsequently reconfigured some of its internal systems, resulting in an immediate decline of queries for .CBA observed at A and J root servers.
Prior to the 2018 KSK rollover, several operators of DNSSEC-validating name servers appeared to be sending out-of-date RFC 8145 signals to root name servers. To ensure the KSK rollover did not disrupt internet name resolution functions for billions of end users, Verisign augmented ICANN’s outreach effort and conducted a multi-faceted technical outreach program by contacting and working with The United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT) and other national CERTs, industry partners, various DNS operator groups and performing direct outreach to out-of-date signalers. The ultimate success of the KSK rollover was due in large part to outreach efforts by ICANN and Verisign.
In response to the ICANN Board’s request in resolutions 2017.11.02.29 – 2017.11.02.31, the ICANN Security and Stability Advisory Committee (SSAC) was asked to conduct studies, and to present data and points of view on collision strings, including specific advice on three higher risk strings: .CORP, .HOME and .MAIL. While Verisign is actively engaged in this Name Collision Analysis Project (NCAP) developed by SSAC, we are also reviving and expanding our 2012 name collision outreach efforts.
Verisign’s name collision outreach program is based on the guidance we provided in several recent peer-reviewed name collision publications, which highlighted various name collision vulnerabilities and examined the root causes of leaked queries and made remediation recommendations. Verisign’s program uses A and J root name server traffic data to identify high-affinity strings related to particular networks, as well as high query volume strings that are contextually associated with device manufacturers, software, or platforms. We then attempt to contact the underlying parties and assist with remediation as appropriate.
While we partially rely on direct communication channel contact information, the key enabler of our outreach efforts has been Verisign’s relationships with the broader collective DNS community. Verisign’s active participation in various industry organizations within the ICANN and DNS communities, such as M3AAWG, FIRST, DNS-OARC, APWG, NANOG, RIPE NCC, APNIC, and IETF1, enables us to identify and communicate with a broad and diverse set of constituents. In many cases, participants operate infrastructure involved in name collisions. In others, they are able to put us in direct contact with the appropriate parties.
Through a combination of DNS traffic analysis and publicly accessible data, as well as the rolodexes of various industry partnerships, across 2020 we were able to achieve effective outreach to the anonymized entities listed in Table 1.
| Organization | Queries per Day to A & J | Status | Number of Collision Strings (TLDs) | Notes / Root Cause Analysis |
| Search Engine | 650M | Fixed | 1 string | Application not using FQDNs |
| Telecommunications Provider | 250M | Fixed | N/A | Prefetching bug |
| eCommerce Provider | 150M | Fixed | 25 strings | Application not using FQDNs |
| Networking Manufacturer | 70M | Pending | 3 strings | Suffix search list |
| Cloud Provider | 64M | Fixed | 15 strings | Suffix search list |
| Telecommunications Provider | 60M | Fixed | 2 strings | Remediated through device vendor |
| Networking Manufacturer | 45M | Pending | 2 strings | Suffix search list problem in router/modem device |
| Financial Corporation | 35M | Fixed | 2 strings | Typo / misconfiguration |
| Social Media Company | 30M | Pending | 9 strings | Application not using FQDNs |
| ISP | 20M | Fixed | 1 string | Suffix search list problem in router/modem device |
| Software Provider | 20M | Pending | 50+ strings | Acknowledged but still investigating |
| ISP | 5M | Pending | 1 string | At time of writing, still investigating but confirmed it is a router/modem device |
Many of the name collision problems encountered are the result of misconfigurations and not using fully qualified domain names. After operators deploy patches to their environments, as shown in Figure 1 below, Verisign often observes an immediate and dramatic traffic decrease at A and J root name servers. Although several networking equipment vendors and ISPs acknowledge their name collision problems, the development and deployment of firmware to a large userbase will take time.
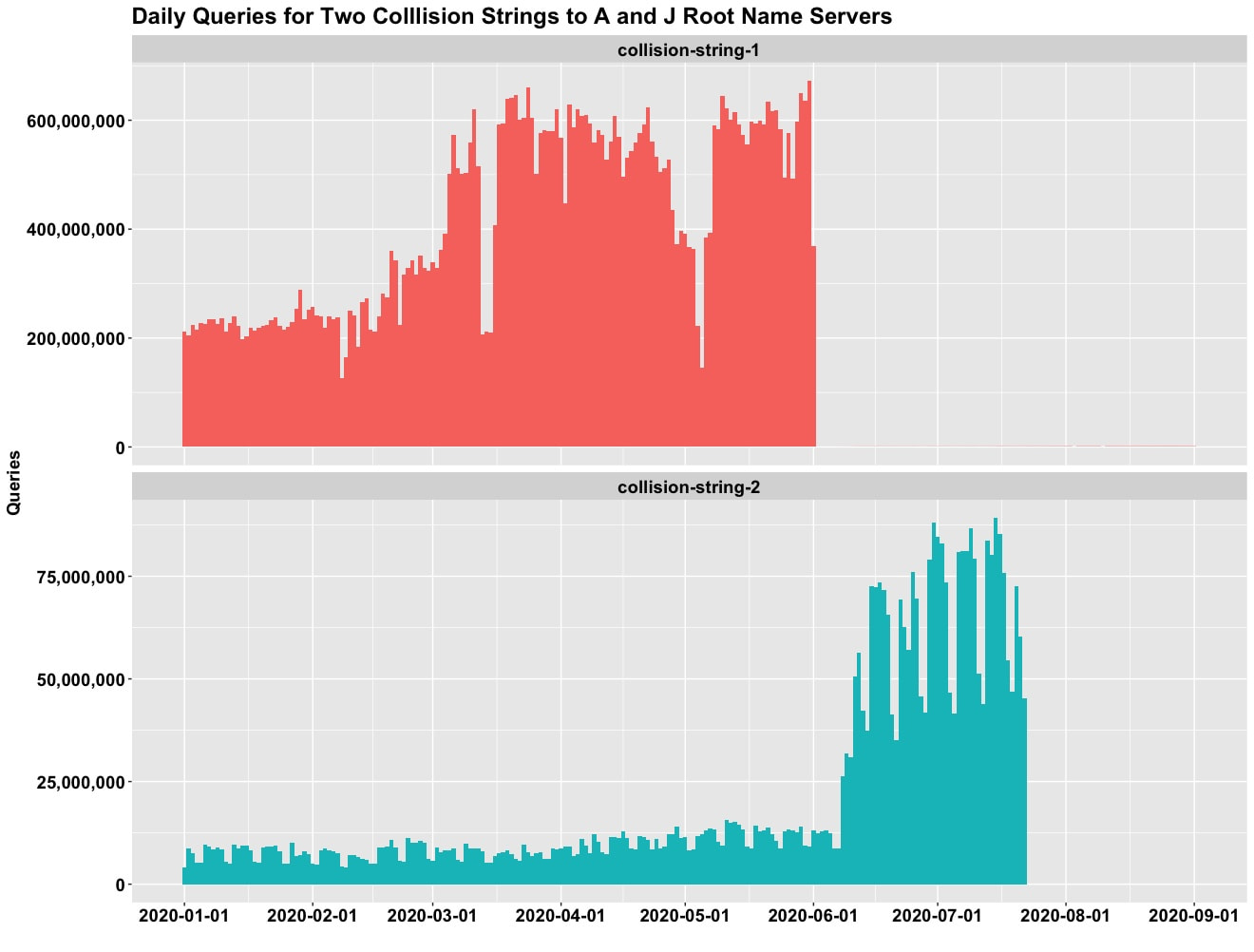
Cumulatively, the operators who have deployed patches constitute a reduction of one billion queries per day to A and J root servers (roughly 3% of total traffic). Although root traffic is not evenly distributed among the 13 authoritative servers, we expect a similar impact at the other 11, resulting in a system-wide reduction of approximately 6.5 billion queries per day.
As the ICANN community prepares for Subsequent Procedures (the introduction of additional new TLDs) and the SSAC NCAP continues to work to answer the ICANN Board’s questions, we encourage the community to participate in our efforts to address name collisions through active outreach efforts. We believe our efforts show how outreach can have significant impact to both parties and the broader community. Verisign is committed to addressing name collision problems and will continue executing the outreach program to help minimize the attack surface exposed by name collisions and to be a responsible and hygienic root operator.
For additional information about name collisions and how to properly manage private-use TLDs, please see visit ICANN’s Name Collision Resource & Information website.
1. The Messaging, Malware and Mobile Anti-Abuse Working Group (M3AAWG), Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST), DNS Operations, Analysis, and Research Center (DNS-OARC), Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), North American Network Operators’ Group (NANOG), Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC), Asia Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC), Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)



